Python如何實現線性回歸和批量梯度下降法-創新互聯
這篇文章主要介紹了Python如何實現線性回歸和批量梯度下降法,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
成都創新互聯公司成立與2013年,先為萬秀等服務建站,萬秀等地企業,進行企業商務咨詢服務。為萬秀企業網站制作PC+手機+微官網三網同步一站式服務解決您的所有建站問題。示例
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
class dataMinning:
datasets = []
labelsets = []
addressD = '' #Data folder
addressL = '' #Label folder
npDatasets = np.zeros(1)
npLabelsets = np.zeros(1)
cost = []
numIterations = 0
alpha = 0
theta = np.ones(2)
#pCols = 0
#dRows = 0
def __init__(self,addressD,addressL,theta,numIterations,alpha,datasets=None):
if datasets is None:
self.datasets = []
else:
self.datasets = datasets
self.addressD = addressD
self.addressL = addressL
self.theta = theta
self.numIterations = numIterations
self.alpha = alpha
def readFrom(self):
fd = open(self.addressD,'r')
for line in fd:
tmp = line[:-1].split()
self.datasets.append([int(i) for i in tmp])
fd.close()
self.npDatasets = np.array(self.datasets)
fl = open(self.addressL,'r')
for line in fl:
tmp = line[:-1].split()
self.labelsets.append([int(i) for i in tmp])
fl.close()
tm = []
for item in self.labelsets:
tm = tm + item
self.npLabelsets = np.array(tm)
def genData(self,numPoints,bias,variance):
self.genx = np.zeros(shape = (numPoints,2))
self.geny = np.zeros(shape = numPoints)
for i in range(0,numPoints):
self.genx[i][0] = 1
self.genx[i][1] = i
self.geny[i] = (i + bias) + random.uniform(0,1) * variance
def gradientDescent(self):
xTrans = self.genx.transpose() #
i = 0
while i < self.numIterations:
hypothesis = np.dot(self.genx,self.theta)
loss = hypothesis - self.geny
#record the cost
self.cost.append(np.sum(loss ** 2))
#calculate the gradient
gradient = np.dot(xTrans,loss)
#updata, gradientDescent
self.theta = self.theta - self.alpha * gradient
i = i + 1
def show(self):
print 'yes'
if __name__ == "__main__":
c = dataMinning('c:\\city.txt','c:\\st.txt',np.ones(2),100000,0.000005)
c.genData(100,25,10)
c.gradientDescent()
cx = range(len(c.cost))
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(cx,c.cost)
plt.ylim(0,25000)
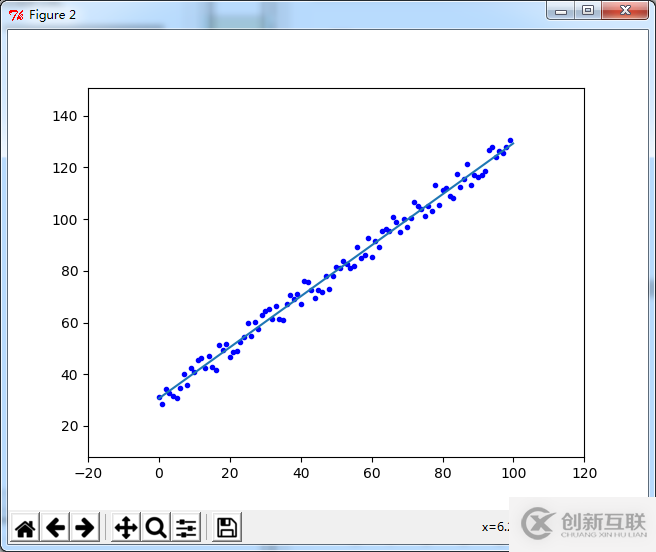
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(c.genx[:,1],c.geny,'b.')
x = np.arange(0,100,0.1)
y = x * c.theta[1] + c.theta[0]
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.margins(0.2)
plt.show()
圖1. 迭代過程中的誤差cost
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Python如何實現線性回歸和批量梯度下降法”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持創新互聯成都網站設計公司,關注創新互聯成都網站設計公司行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
另外有需要云服務器可以了解下創新互聯scvps.cn,海內外云服務器15元起步,三天無理由+7*72小時售后在線,公司持有idc許可證,提供“云服務器、裸金屬服務器、網站設計器、香港服務器、美國服務器、虛擬主機、免備案服務器”等云主機租用服務以及企業上云的綜合解決方案,具有“安全穩定、簡單易用、服務可用性高、性價比高”等特點與優勢,專為企業上云打造定制,能夠滿足用戶豐富、多元化的應用場景需求。
網頁名稱:Python如何實現線性回歸和批量梯度下降法-創新互聯
網頁地址:http://vcdvsql.cn/article8/cdigip.html
成都網站建設公司_創新互聯,為您提供建站公司、自適應網站、品牌網站建設、品牌網站設計、網站改版、網站設計公司
聲明:本網站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如需處理請聯系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內容未經允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創新互聯

- A5營銷:網站“抓取異常”問題的解決方案 2020-08-24
- 響應和解決方案的挑戰 2016-08-12
- 網絡營銷網站建設解決方案 2023-01-05
- 地方網站運營之常見問題和解決方案篇 2021-01-09
- 成都網站建設解決方案 2020-02-23
- 手機品牌網站分析及開發解決方案 2023-03-06
- 學校網站建設解決方案是針對哪些 2015-10-11
- SEO過度優化的解決方案 2023-04-06
- 【網站建設】如何制定符合網站SEO優化的解決方案? 2022-04-29
- 展示型網站解決方案 2013-07-27
- 醫院網站制作解決方案 2021-12-26
- 上市公司網站建設的解決方案 2015-02-14