updateStateByKey與mapwithstate怎么實現
這篇文章主要講解了“updateStateByKey與mapwithstate怎么實現”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“updateStateByKey與mapwithstate怎么實現”吧!
成都創新互聯-專業網站定制、快速模板網站建設、高性價比清徐網站開發、企業建站全套包干低至880元,成熟完善的模板庫,直接使用。一站式清徐網站制作公司更省心,省錢,快速模板網站建設找我們,業務覆蓋清徐地區。費用合理售后完善,十多年實體公司更值得信賴。
updateStateByKey與mapwithstate 這兩個方法在Dstream中是找不到的,他們是通過隱式轉換來進行實現的

由此可以看到,最終是通過PairDStreamFunctions來實現這兩個方法的。
updateStateByKey

newUpdateFunc 方法是在原有基礎上如何進行更新的方法
defaultPartitioner()獲得默認的分區數

如下代碼出現了一個非常關鍵的地方
new StateDStream(self, ssc.sc.clean(updateFunc), partitioner, rememberPartitioner, None)

StateDStream 繼承自Dstream。
stateDStream自會持久化到內存中
里面有一個很總要的方法:如果存在parent RDD 就將執行computeUsingPreviousRDD方法

在該方法中,有一處性能瓶頸的代碼

每次進行更新的時候都會將原有的parentRDD進行cogroup,這樣程序不斷的運行這樣會導致越來越慢!盡量少用改方法!

Mapwithstate
mapWithState方法的返回值是MapWithStateDStream,我們來看看它的實現類
MapWithStateDStreamImpl

最終返回InternalMapWithStateDStream

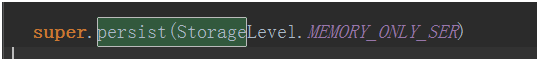
跟updateStateByKey一樣是持久化在了內存中
persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY)
接下來看看每個繼承自Dstream的最重要的方法 compute:

最終操作的是RDD:MapWithStateRDD
RDD中的partition被MapWithStateRDDRecord代表

MapWithStateRDDRecord有伴生對象:中的方法,該方法是對state進行更新操作,不像 updateStateByKey每次都會進cogroup的操作,而是在原有的基礎上進行更新,效率得到了提高!
defupdateRecordWithData[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, S: ClassTag, E: ClassTag](
prevRecord: Option[MapWithStateRDDRecord[K, S, E]],
dataIterator: Iterator[(K, V)],
mappingFunction: (Time, K, Option[V], State[S]) => Option[E],
batchTime: Time,
timeoutThresholdTime: Option[Long],
removeTimedoutData: Boolean
): MapWithStateRDDRecord[K, S, E] = {
// Create a new state map by cloning the previous one (if it exists) or by creating an empty one
valnewStateMap = prevRecord.map { _.stateMap.copy() }. getOrElse { newEmptyStateMap[K, S]() }
valmappedData = newArrayBuffer[E]
valwrappedState = newStateImpl[S]()
// Call the mapping function on each record in the data iterator, and accordingly
// update the states touched, and collect the data returned by the mapping function
dataIterator.foreach { case(key, value) =>
wrappedState.wrap(newStateMap.get(key))
valreturned = mappingFunction(batchTime, key, Some(value), wrappedState)
if(wrappedState.isRemoved) {
newStateMap.remove(key)
} else if(wrappedState.isUpdated
|| (wrappedState.exists && timeoutThresholdTime.isDefined)) {
newStateMap.put(key, wrappedState.get(), batchTime.milliseconds)
}
mappedData ++= returned
}
// Get the timed out state records, call the mapping function on each and collect the
// data returned
if(removeTimedoutData && timeoutThresholdTime.isDefined) {
newStateMap.getByTime(timeoutThresholdTime.get).foreach { case(key, state, _) =>
wrappedState.wrapTimingOutState(state)
valreturned = mappingFunction(batchTime, key, None, wrappedState)
mappedData ++= returned
newStateMap.remove(key)
}
}
MapWithStateRDDRecord(newStateMap, mappedData)
}
}
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“updateStateByKey與mapwithstate怎么實現”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對updateStateByKey與mapwithstate怎么實現這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是創新互聯,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
新聞標題:updateStateByKey與mapwithstate怎么實現
當前URL:http://vcdvsql.cn/article24/ggheje.html
成都網站建設公司_創新互聯,為您提供動態網站、ChatGPT、用戶體驗、網站導航、標簽優化、面包屑導航
聲明:本網站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如需處理請聯系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內容未經允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創新互聯

- 韓國虛擬主機怎么樣?韓國虛擬主機有哪些優點? 2022-10-05
- vps主機不能取代虛擬主機的四大理由 2022-10-10
- 成都使用虛擬主機的三大好處 2023-02-26
- 虛擬主機訪問不了,虛擬云主機訪問慢怎么辦? 2022-10-08
- 選擇網站虛擬主機要注意什么 2022-10-04
- 云服務器跟虛擬主機要怎么區分? 2022-10-02
- 東莞服務器和東莞虛擬主機租用哪個好? 2022-10-03
- 新加坡虛擬主機穩定嗎 2022-10-12
- 虛擬主機建站有什么好處 2022-07-06
- 告訴你如何判斷虛擬主機的好壞 2016-09-22
- 云虛擬主機和云服務器如何區別 2021-02-14
- 如何選擇適合自己的云主機?云主機和虛擬主機有何不同? 2022-10-02